
Our mission is to improve patient outcomes and reduce the cost of care. Masimo (NASDAQ: MASI) is a global medical technology company that develops and produces a wide array of industry-leading monitoring technologies, including innovative measurements, sensors, patient monitors, and automation and connectivity solutions. As the current study and others have found, processed EEG monitoring during surgery, by helping clinicians minimize the duration of burst suppression, may lower the rate of POD. The incidence of POD has been associated both with preoperative vulnerabilities and-of key importance to studies such as this-the cumulative duration of intraoperative EEG burst suppression. , dedicated to minimizing the impact of pre-existing cognitive deficits and optimizing the cognitive recovery and perioperative experience for adults 65 years and older undergoing surgery, describes POD as a “major public health issue.” 14 POD is associated both with worse short- and long-term outcomes and higher costs, 3,6-9Īnd numerous medical bodies-including the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), the United Kingdom National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, the American Geriatric Society, and the American College of Surgeons-have made the prevention of POD a public health priority. A common and serious complication, POD afflicts up to 60% of patients after major surgery, 2-5Īnd occurs in up to 91% of the critically ill. Postoperative delirium is an acute state of mental confusion characterized by alterations in attention, consciousness, and disorganized thinking. Patients, especially those exhibiting hemodynamic fluctuations or receiving surgical procedures that disrupt cerebral perfusion, may benefit from the monitoring of multiple EEG parameters during surgery.” The researchers concluded, “Processed electroencephalogram-guided general anesthesia management, consisting of PSi combined with DSA monitoring, can significantly reduce the risk of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing CEA. There was no significant difference in the incidence of other neurologic complications. Patients in the intervention group also spent significantly less overall time with EEG suppression. The researchers found that the incidence of POD was significantly lower in the intervention group (7.87% of patients) compared to the standard group (28.91% of patients, p < 0.01). A team of neurophysiologists independently reviewed the EEG data acquired by SedLine to calculate the cumulative duration of burst suppression for each patient. Secondary outcomes were postoperative hospital length of stay (LOS) and other neurologic complications.


The primary outcome was the incidence of POD, measured using the Confusion Assessment Method, during the first three days after surgery.
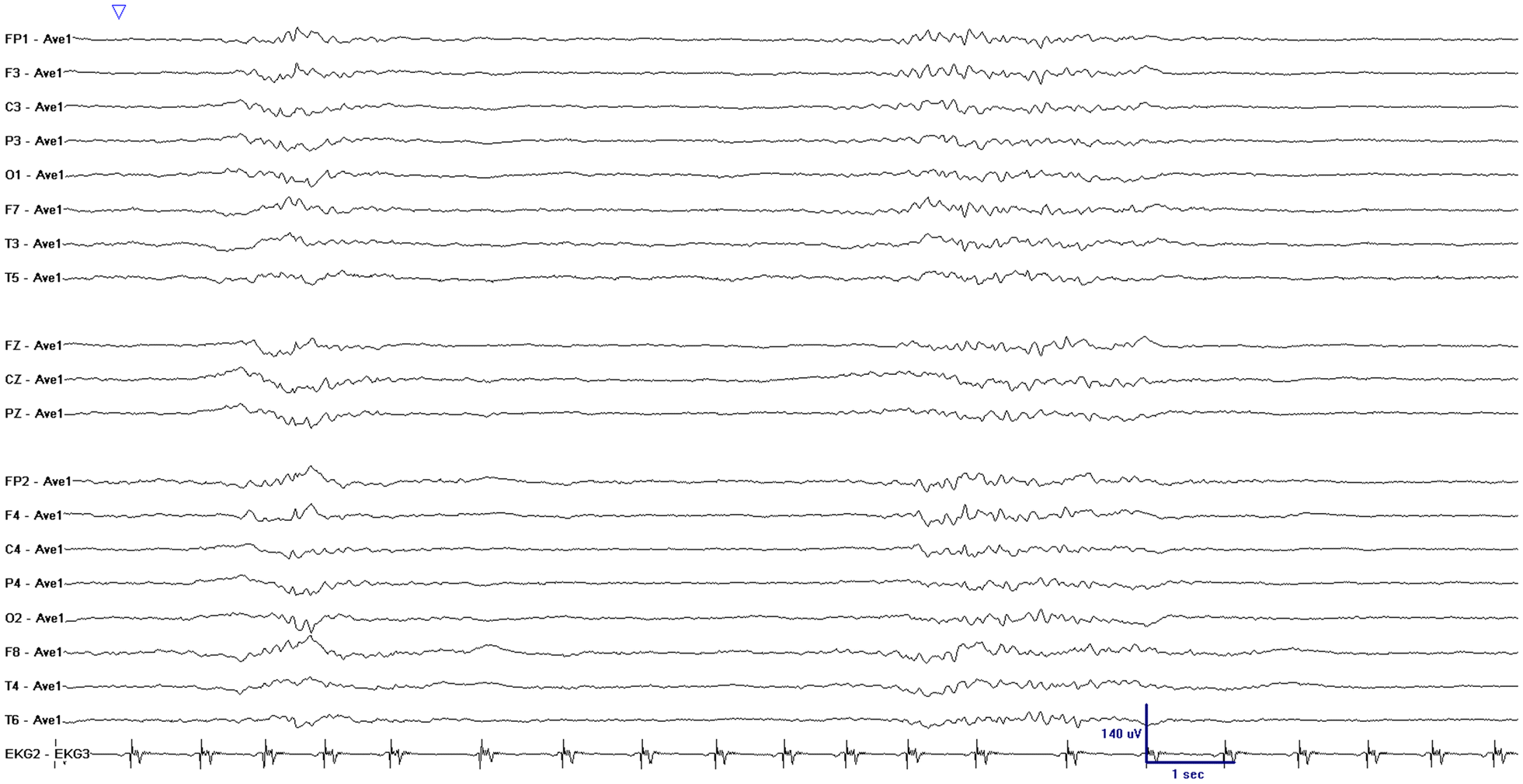
In both groups, patients were also monitored with continuous transcranial Doppler ultrasound and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) (designed to avoid perioperative cerebral hypoperfusion or hyperperfusion).
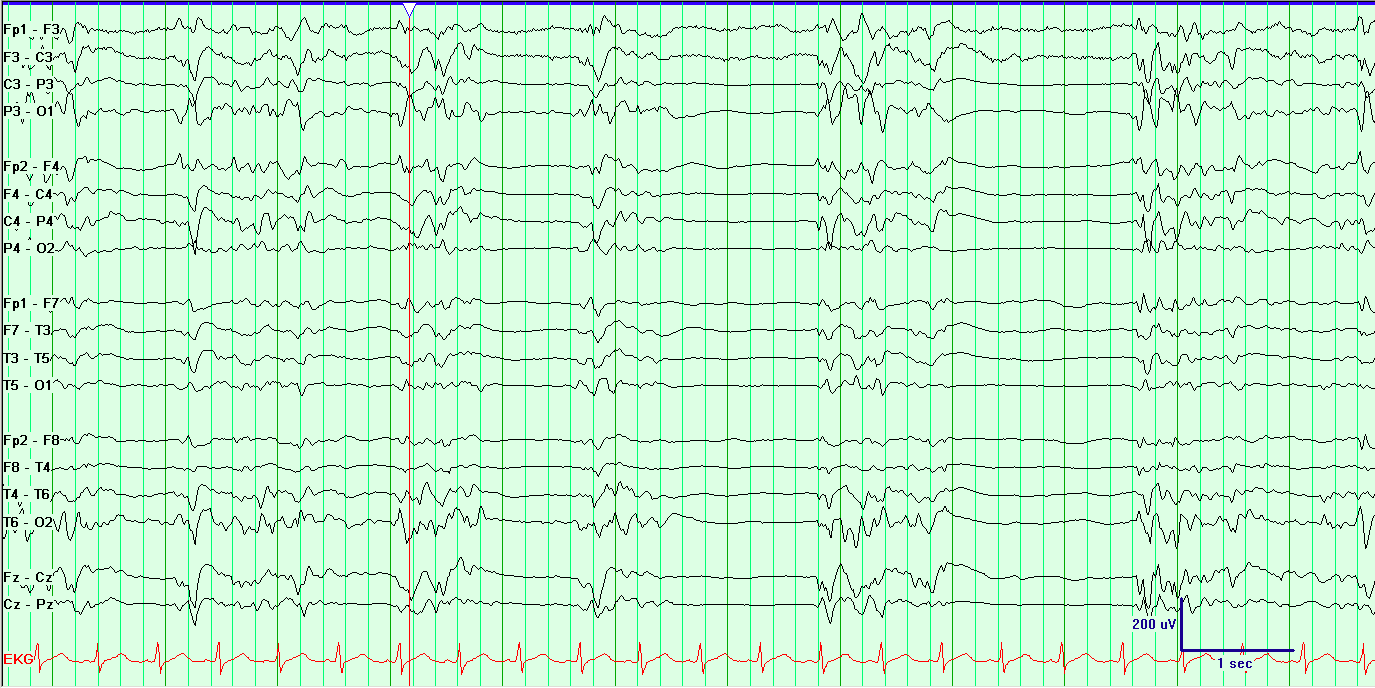
In the intervention group, general anesthesia was managed using a combination of Masimo SedLine PSi and DSA monitoring (designed to reduce the risk of intraoperative EEG burst suppression) in the standard group, PSi without DSA monitoring was used. The authors enrolled 255 patients scheduled for CEA and divided them randomly into an intervention group (n=127, mean age 62) and a standard group (n=128, mean age 63). Noting that the incidence of POD is associated with the duration of EEG suppression during surgery, they sought to investigate whether monitoring multiple processed EEG parameters simultaneously to guide anesthesia during a procedure like CEA could positively impact the incidence of POD, compared to use of a single parameter alone. POD is a “common yet serious” type of geriatric neurological dysfunction associated with worse short- and long-term prognosis and higher healthcare costs. The researchers noted that cerebral blood supply may be “severely disrupted” during CEA, the gold standard treatment for severe carotid stenosis, and that cerebral function is “highly vulnerable” to even brief changes in oxygen and blood supply, as well as to cerebral vascular diseases like carotid stenosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
